Air Dispersion Modelling for Industrial Emissions and Planning

What is Air Dispersion Modelling?
Air dispersion modelling is the mathematical representation of pollutant movement and the diffusion processes from industrial air emission sources which occur in the atmosphere under predefined conditions.
Air dispersion modelling is commonly used to predict the concentration of downstream ground-level pollutants from industrial sources in the surrounding environment in terms of air quality. Air dispersion models are regularly developed as part of planning applications, EIAR assessments, plant design, modifications of existing facilities, appraisal/evaluation of existing abatement strategies etc. For example, at the design phase of a project, dispersion modelling can be employed to establish the most suitable location, stack (flue) height and emission parameters for single or multiple sources. Many diverse emission scenarios can be modelled to ascertain the most suitable approach for emission management at the installation.
Factors Influencing Air Pollutant Dispersion
Dispersion and movement of air pollutants in the atmosphere are affected by numerous factors, which include local terrain, global and regional meteorological conditions, site building layout, land use etc. It’s important to note that wind speed and wind direction are amongst the most important input data when generating an air dispersion model i.e., prevailing wind systems.
Air dispersion models use this detailed input data to process various algorithms establishing the dispersion of pollutants between the source and receptor. The model then determines the predicted time-averaged concentration at selected receptors and/or within a defined grid. Projected concentrations are added to background concentrations and then evaluated against associated ambient air quality standards and guidelines. The geographical variations in ground-level pollutant concentrations beyond the facility boundary for worst-case scenarios modelled can then be illustrated as concentration contours.
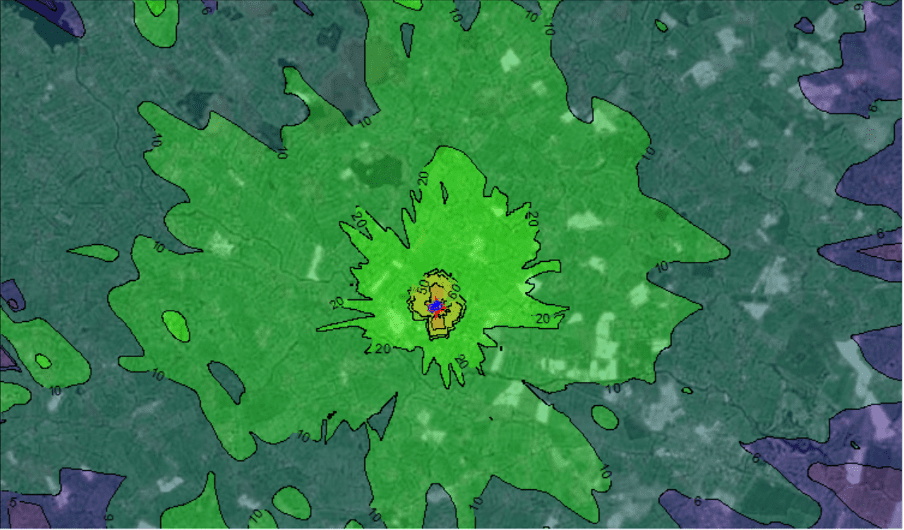
Figure 1: Predicted geographical variations in ground level pollutant concentrations
EPA Guidance and Air Dispersion Modelling Methodology
Assessments are conducted in accordance with the EPA guidance document, Air Dispersion Modelling from Industrial Installations Guidance Note (AG4) for standard air pollutants i.e. NOx, SO2, CO, PM10 etc. and where applicable for odour i.e. Odour Emissions Guidance Note (Air Guidance Note AG9).
For estimating the impact of non-reactive pollutants, the most widely used dispersion technique relies on Gaussian models. The term “Gaussian” refers to the statistical concept in which a group of arranged values follows a bell-shaped curve distribution. This type of arrangement is typically known as a “normal distribution.”
AERMOD is an up-to-date air dispersion model based on planetary boundary layer theory. It is a steady-state Gaussian plume model used to assess pollutant concentrations from a wide variety of sources associated with industrial emissions which was developed by the American Meteorological Society (AMS) and the United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA). It utilises building downwash algorithms, advanced depositional parameters, local terrain effects, and advanced meteorological turbulence calculations. Key features include settling and dry deposition of particles; building downwash; point, area, line, open pit, flare, and volume sources; flat and complex terrain.
AERMOD is recommended for use in the Irish EPA AG4 guidance as well as by the US EPA and is commonly used in Ireland for air dispersion modelling of point source emissions from licensed facilities. AERMOD is applicable to rural and urban areas flat and complex terrain surfaces and elevated releases and multiple sources including point area and volume sources.
Air Dispersion Modelling Software and Assessment Process
As per EPA guidance within the AG4 document it is advisable to use a graphical user interface software package in order to prepare an accurate input file for the model. AERMOD View software employed by ORS is an enhanced user interface for AERMOD, Gaussian Plume Air Dispersion Model, created & distributed by Lakes Environmental. AERMOD View provides modelers with the means and functionality necessary to achieve air quality analyses that help to address permitting, regulatory, nuisance issues and sizing/complexity of abatement systems etc.
Below (Figure 2) is an overview of the steps which are usually required in order to undertake an air dispersion modelling assessment from Air Dispersion Modelling from Industrial Installations Guidance Note (AG4).
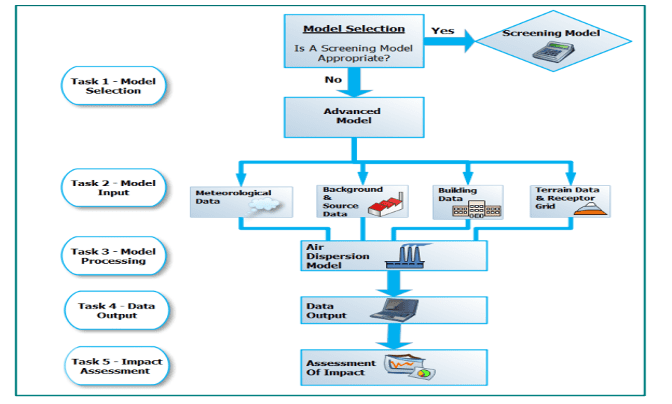
Figure 2: Flowchart of tasks required when undertaking an air dispersion modelling assessment
Get in touch with our Environmental Team at info@ors.ie if you have any queries on air dispersion modelling.
Get in touch with our Environmental Team at info@ors.ie or call +353 1524 2060 if you have any queries on air dispersion modelling.
